How To Find Critical Value In Statcrunch
Objectives
By the end of this lesson, yous will be able to...
- observe critical values of the F-distribution
- test hypotheses regarding ii population standard deviations
For a quick overview of this department, watch this short video summary:
The last parameters we need to compare between 2 populations are the variance and standard divergence. Before we can develop a hypothesis test comparison two population parameters, nosotros need another distribution.
Fisher's F-distribution
Unlike the hateful, the standard deviation is extremely susceptible to farthermost values, and consequently does a very poor job of measuring spread for distributions that are not symmetric. So before we do any inference regarding population standard deviations, we must commencement verify that the samples come from normally distributed populations.
Fisher'due south F-distribution
If ![]() and
and ![]() and
and ![]() are sample variances from independent simple random samples of size due northoneand ntwo, respectively, drawn from normal populations, then
are sample variances from independent simple random samples of size due northoneand ntwo, respectively, drawn from normal populations, then
![]()
follows the F-distribution with n1-1 degrees of liberty in the numerator and
ntwo-1 degrees of liberty in the denominator.
Properties of the F-distribution
- Like the Χ 2 distribution, it is not symmetric. It is skewed right
- The shape depends on the degrees of freedom in the numerator and denominator.
- F ≥0
Discover here that the samples must come from normally distributed populations.
Finding Critical Values
Find critical values in the F-distribution using a table is washed in a similar way to the t and Χ 2 tables, though with some differences. The values in the tabular array still represent values with the indicidated α area to the right, merely because the F distribution has 2 degreees of freedom rather than one, it requires a separate table for each α.
Before we start the section, you need a copy of the table. You tin download a printable copy of this table, or utilize Tabular array VII starting on folio A-14 in the dorsum of your textbook. That table will look unlike than the printable version linked above considering the publisher did non provide a digital version.
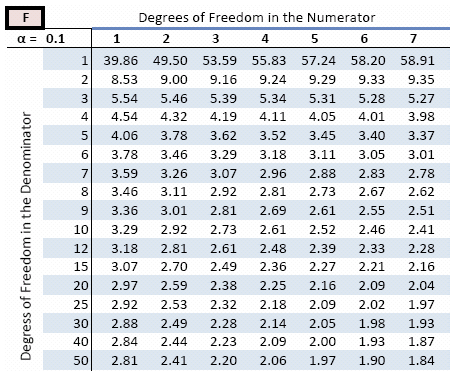
So the values in the table in a higher place are the disquisitional values:
![]()
Yous may wonder how we find critical values for left-tailed tests. To do that, we use the same table and the following formula:
![]()
Let'south try a couple examples.
Example i
Find the value of the F-distribution that has α=0.05 area to the right, with 10 degrees of freedom in the numerator, and fifteen degrees of freedom in the denominator.
[ reveal reply ]
So F 0.05, 10, xv = 2.54
Example ii
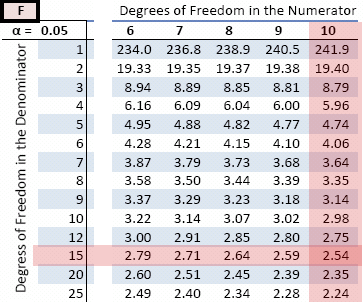
Find the value of the F-distribution that has α=0.05 area to the left, with 20 degrees of freedom in the numerator, and viii degrees of freedom in the denominator.
[ reveal answer ]
| F 0.95, 20, 8 = | 1 | 1 | ≈ 0.41 | |
| F 0.05, eight, twenty | two.45 |
Finding Disquisitional Values Using StatCrunch
Click on Stat > Calculators > F
Enter the numerator and denominator degrees of freedom, the direction of the inequality, and the probability (go out X blank). Then press Compute.
Instance 3
Utilise the technology of your choice to detect the value from the F-distribution with α=0.01 area to the right if samples of size 15 and xx are taken.
[ reveal answer ]
Using StatCrunch:
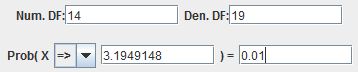
Then F 0.01, 14, 19 = iii.19
Performing a Hypothesis Test Regarding 2 Population Standard Deviations
Footstep 1 : State the null and alternative hypotheses.
Footstep 2 : Decide on a level of significance, α.
Stride 3 : Compute the test statistic, ![]() .
.
Footstep four : Determine the P-value.
Step 5 : Turn down the nix hypothesis if the P-value is less than the level of significance, α.
Stride 6 : Country the conclusion.
Hypothesis Testing Regarding Two Population Standard Deviations Using StatCrunch
- Go to Stat > Variance > Ii Sample > data/summary
- Enter the sample variances or select the appropriate column
- Select Adjacent.
- Ready the null variance ratio (standard is ane) and the alternative hypothesis.
- Click on Calculate.
The results should appear.
Case 4
Problem:In Example i in Section 11.2, we compared the boilerplate scores of men and women on a Mth096 examination. In that test, we assumed that the standard deviations of the 2 groups were equal. Examination the assumption at the α=0.one level of significance.
Solution:
First, we demand to check the conditions. We know from Instance 1 that neither sample contains outliers, but we do not know if they come from normally distributed populations. Nosotros'll use StatCrunch to perform Q-Q plots.
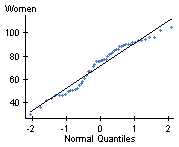
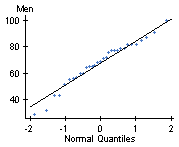
While the ii plots aren't exactly linear, it does appear that the samples could come up from normally distributed populations, so our conditions are satisfied.
Footstep 1 :
H0: ![]()
H1: ![]()
Step 2 : α = 0.1 (given)
Step iii : (we'll employ StatCrunch)
Step 4 : Using StatCrunch:
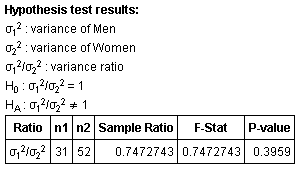
Step 5 : Since the P-value > α, we exercise not reject the nil hypothesis.
Footstep six : Based on these results, at that place is no evidence to support the claim that the standard deviations are not equal.
Source: https://faculty.elgin.edu/dkernler/statistics/ch11/11-4.html
Posted by: schultzasts1995.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Find Critical Value In Statcrunch"
Post a Comment